Some carotid stenosis and occlusions do not present with symptoms. They can be detected by colored Doppler ultrasonographies made for control purposes. However some patients may develop temporary or permanent strokes. This may result in temporary or permanent sight loss, speech disorder and arm and/or leg paralysis. The main reason is the embolization from the plaque which produces the narrowing in the carotid artery, and thus, the stop of circulation at a certain part of the brain. This brain region, which has a circulation disorder, shows function loss. In mild form, these findings are temporary and can be named as temporary ischemic attacks (TIA). In some patients these findings may become permanent. Some patients of this group may be lost while the others can be permanently dependent on patient care.
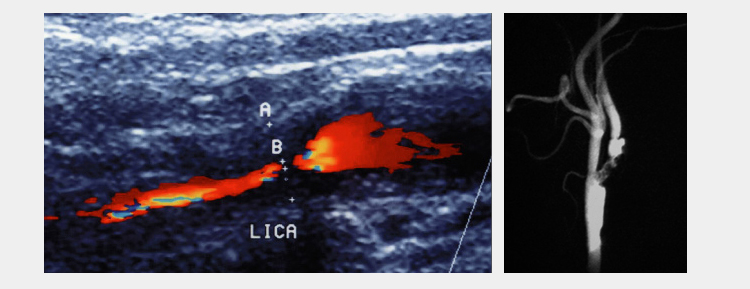
In order to provide an absolute diagnosis based on patient complaints and examination findings, it is necessary to use imaging techniques. Colored Doppler ultrasonography, MR or BT angiography or conventional angiographies are the most commonly used screening methods in diagnosis.
Closed (endovascular stenting) method or open surgery (carotid endarterectomy) are used as treatment modalities according to patient status. Open surgery can be applied with local, or general anesthesia. The plaque, causing the sstenosis, is removed surgically. Generally It is sufficient to have the patient rest at the hospital for 2-3 days. In endovascular method, groin area is anestetized with local anesthesia and inguinal artery are entered by using special needles. Angiography is taken and stenosis is located. A temporary filter is placed to prevent little fractures to enter brain blood circulation before stenting. Then, the stent (metal pipette) is placed on the stenosis area and the stenotic area is opened. Stenting operation is a method that has to be careful in patient selection. Certain patients are not candidate for stenting. It is sufficient to have the patients rest at the hospital for one day.


 | +90 212 375 6565 / 6640
| +90 212 375 6565 / 6640